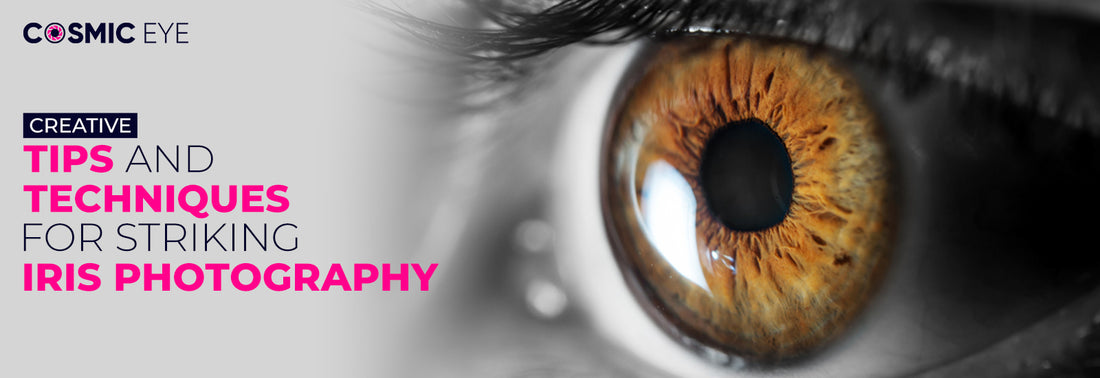
Have you ever been captivated by someone’s eyes? Eyes, the intricate windows of our soul, have long held the allure of photographers and painters. Their mesmerizing patterns, universe of colors, intriguing texture, and expressiveness make them fascinating.
As a result, you can find iris photography featured in a broad spectrum of settings, from creative art projects to editorial shoots.
However, while photographing an eye close-up can be a rewarding experience, nailing it can be daunting. Photographing iris is a part of macro photography, which requires excellent attention to detail, unique tools, specific camera settings, and fundamental editing skills.
In today’s blog, we cover all of that and more tips for extraordinary iris photography.
So, if you are looking to brush up your micro photography skills, dive into the following section now!
What Is Iris Photography?
Eye iris photography, also known as ocular photography, is a specialized photography genre capturing the unique beauty and details of human, insect, or animal eyes. It combines commercial, fine art, and micro photography to take stunning, high-quality close-up shots or portraits of eyelashes or irises.
Iris photography has been used for ages, from creating unforgettable memories during a wedding to diagnosing eye conditions as a part of medical photography.
Eyes provide a point of interest to photographers, carrying unique characteristics you cannot replicate. It will not just captivate and draw in your viewers but become a timeless piece of art that will remain with your clients forever.
Essential Equipment For Best Iris Shot
Lucky for you, compared to other forms of photography, taking a picture of an iris requires much less investment. You only need a handful of tools that most photographers have.
Here’s covering all the essential equipment required for the best iris shot!
-
Camera
A functional camera is one of the first things you need for photography. You will need a high-resolution camera with interchangeable lenses to perfectly capture the complexities and emotions of iris pictures.
Before purchasing a camera for iris photos, ensure it supports macro lenses.
-
Macro Lens
The dimensions of the iris can range between 11 to 13mm. Therefore, you will need a specific lens type to capture its details. The most used lens for iris photography is the macro lens. These lenses are critical for getting close-up shots of the eye.
However, there are specific details you will need to be aware of when purchasing macro lenses. For instance, the lenses you buy should have at least 1:1 magnification. Also, maintain a reasonable working distance of between 20 and 30 cm.
-
Lighting
Lighting is among the most problematic parts to resolve when capturing the eye of the iris. You need to choose which equipment will be best to bring out the color of the iris and light it up just enough to photograph the details.
We recommend 2 tiny, flexible light sources: natural light and a camera flash. When using natural light, you can use v-flat to fill the light and scrip to diffuse it. Furthermore, consider investing in a ring flash if you need constant light.
Also, you should learn how light influences the parameters of your camera (e.g., aperture, ISO, and white balance), pupil size, and iris color before using the tools.
-
Tripod, Camera Mount, and Head Stabilization
A steady hand is another vital component of capturing iris pics. However, keeping your hands steady can be challenging when photographing moving objects. Hence, we recommend using a tripod or a similar tool to mount the camera.
Additionally, you can use a chin rest, professional headstands, or even books to give clients a place to rest their heads and reduce micro-movements.
-
Adjustment Rails and Head Shroud
Use a manual focus staking rail to adjust your camera’s lateral and vertical movement. It will help you fine-tune the camera’s placement to match eye movement.
Furthermore, if you don’t want external light sources to ruin your iris art, use boxes to surround the subject. It will keep out external reflections and provide privacy to the person you are about to photograph.
Camera Settings to Achieve Captivating Iris Photos
Producing magical eyeball photography doesn’t end with buying some equipment. You need to know how to work these tools, particularly the camera settings, to bring out the swirling details of the eyes.
Below, we reveal five crucial camera settings and processes for iris photography to take your shots from ordinary to extraordinary.
-
Mode
Camera modes refer to the controls that photographers pick before shooting a subject. The mode you choose influences the core settings of a camera, such as aperture, ISO, and shutter speed, helping photographers obtain sufficient exposure.
Moreover, there are several types of camera modes for different photographs. Most experts recommend Av/A or Aperture Priority Mode and Manual Mode (M) for iris shots.
i) Aperture Priority Mode (Av/A):
It allows the camera to automatically set the shutter speed while you set the aperture (f-stop). A wide aperture, such as f/2.8, creates a shallow field depth to isolate the iris from the background. However, a wide aperture also requires additional settings to maintain proper exposure.
ii) Manual Mode (M):
Manual mode will give you complete control over camera exposure. However, adjusting both shutter speed and aperture manually can be time-consuming.
-
Aperture
In photography, aperture refers to the adjustable lens opening that controls the amount of light a camera receives.
It’s typical to have a very shallow depth of field in macro photography, which indicates how much of your scene is in focus. Therefore, you need the correct aperture to lock in the focus.
Experts suggest avoiding large aperture, such as f/1.8, unless you aim to create a shallow depth of field. To enhance the focus on the iris of the eye picture, you can instead use a narrow aperture, like f/8 or f/11.
The narrow aperture will widen the focus area and improve the depth of field, ensuring the iris remains the picture's hero.
-
Shutter Speed
During macro photography, you can simply ask your model to stay still or give them a prop, such as a chin rest, to stabilize their head. That’s why, for the most part, shutter speed doesn’t play a role as crucial as the aperture here.
Still, even if you don’t need a breakneck shutter speed, try not to go below 1/60 s. The human eyes are always eager to move and look around. So, you can expect slight movement.
Furthermore, if you are capturing animal eyes, you will need a fast shutter speed. Otherwise, you might get motion blur.
If you are confused about the shutter speed ideal for the shoot, you can use Aperture Priority mode and let your camera automatically pick the shutter speed. Alternatively, some photographers use Manual mode to use dissimilar shutter speeds for different shoots.
Lastly, if you use a faster shutter speed, consider adding additional, soft, diffuse lights instead of flash. A flash can be too harsh for the eyes.
-
ISO
One of the crucial camera settings that often gets overlooked when capturing an iris-of-eye picture is ISO.
ISO is a standard unit of measurement that dictates how sensitive the camera sensor is to light. Increasing the ISO number can brighten up the photos and give you more control over the aperture and shutter speed. However, raising the ISO can introduce more noise, reducing the image's sharpness and quality.
If you wish to ensure your picture of the eye iris looks sharp, try adjusting the ISOs manually. Experts generally advise using your lowest ISO (typically around ISO 100). However, some cameras support shooting noise-free images up to ISO 1600.
If you are using a fast shutter speed, narrow aperture, or shooting in low light, you may have no choice but to shoot with a higher ISO. In those events, you can use Photoshop to remove the noise.
-
Focus
When it comes to macro photography, precision is key. To maintain this precision, most photographers recommend using manual focus. The reason is simple: Manual modes ensure the iris remains sharply in focus while the rest of the photograph stays pleasantly blurry.
Another reason for using manual focus is that automatic iris aperture focus with the lens wide open only stops at the chosen aperture for a few seconds when you take the shot.
However, when you focus manually with the camera, you will have direct control over the clarity and sharpness of the focused area. It will empower you to intentionally manipulate the focus and effortlessly capture the intricate details of the iris.
Yet, if you struggle to keep up with the iris's movement, you can try auto-capture to make the job easier.
Tips & Techniques for Eyeball Photography
Eye photography lets us get an up-close view of something we rarely see in detail. However, capturing these incredible photos requires some specific techniques.
Now that you know the fundamentals of iris photography, grasping these techniques will be much easier.
So, let’s look at some professional tips and techniques recommended for iris photography.
-
Focus and Depth of Field
As we have mentioned before, the depth of field will influence the sharpness of your picture of the eye iris. If you wish to catch the tiny details of a human or animal eye, use a narrow aperture within the range of f/8 to f/11. At the same time, don’t shy away from experimenting with shallow depth of field to create visually stunning eye imagery.
Additionally, utilize microlenses for extreme close-ups to capture the hypnotizing details of the eyelashes, veins, and iris.
As for focus, we recommend manual focus when there’s a lack of movement and effortlessly controlling where the sharpness lands. Different apertures were also experimented with to balance background blur and sharpness.
-
Lighting Techniques
Soft, diffused lighting can help eliminate harsh shadows from your pictures of the iris of the eye. Whether your lighting source is a window or a softbox, it can add a natural, flattering look to the picture. Furthermore, you can use modifiers, like a translucent umbrella or a scrim, to further soften the image.
Additionally, if you want to add a spark or highlight in the eye, strategically position your light source to create a complimenting catch light.
You can also experiment with different angles and light directions to see how they influence the mood and reveal details in the eye.
For instance, you can ask the subject to directly face a light source, such as a window, a ring light, or a diffused light panel to illuminate the eye’s details. Alternatively, you can place the light above or on the subject's side to create more dimension and depth in the eye color and texture.
-
Model Comfort and Eye Safety
The white part of the eye, also known as sclera, is sensitive. Too much stress during iris photography can turn the eye red and puffy, making your photographs off-putting.
Whether you want to include the sclera in your iris shot, we recommend communicating with your client and ensuring they are stress-free and well-rested. Avoiding staring at phone or computer screens is an excellent way to keep the eyes stress-free.
Additionally, you can ask your client to take breaks between the shoots and avoid using bright lights or direct flashes into the eye.
-
Background Choices
Iris photographs aim to draw viewers to the magnificent beauty of our irises. Therefore, backgrounds tend to be simple yet contrasting to the hero of the image.
With most iris art, you will notice a simple, solid background, such as black, that draws attention to the eye.
If you wish to add more interest to the background, consider using the Bokeh technique, which uses a shallow depth of field to create an aesthetically pleasing backdrop. For a bold background, you can use minimalistic digital abstract or abstract patterns.
Post Processing of Iris Art
Once you successfully capture the iris, your next steps shall focus on editing and processing the images. Good editing is a must for optimal results in photography. It will help you bring out the eye's color, soften or sharpen the edges, highlight its unique features, and create a timeless piece of art.
So, read on to find the most effective tips for post-processing iris art.
-
Cropping
Getting close to the iris can be tricky, even if using a microlens with a long focal length. So, once you have taken iris pictures, zoom in to assess whether you can still see the sclera. If you can spot the white part of the eye, consider cropping it out.
All you have to do is clip out the parts of the image and use a cropping tool to reframe the shot. Also, you can use this opportunity to recompose the image if required. Putting the iris at the center of the image is not always necessary. Hence, feel free to experiment with different compositions.
However, remember not to overcrop as it can negatively impact the quality of the image, leading to grainy and pixelated pictures.
-
Color Adjustment and Retouching
The color temperature of your iris pics can significantly impact its appearance. Thus, don’t forget to adjust the white balance to ensure the eye colors are vibrant and accurate.
Furthermore, if you notice any spots, stray hairs, and blemishes around the eyes, consider using a spot removal tool to edit them out with Photoshop.
-
Selective Sharpening
If you wish to make your iris shot sharper or more realistic, use tools like the Clarity slider to enhance the details of the picture. This will increase the clarity of the image, making the colors and veins stand out even more.
You can also use sharpening tools to add crispness to the image, particularly the iris and the eyelashes.
-
Exposure
Another tool that enables you to modify specific parts of your image is the Adjustment Brush in Lightroom. You can use it to increase clarity, saturation, and sharpness. The brush can also help you selectively darken or lighten particular parts of the eye iris photography to add a more dramatic effect.
Additionally, you can employ exposure adjustment tools to darken or brighten the overall image. However, you must be careful not to overexpose the whites of the eyes.
If you wish to add more depth to the image, the Radial Filter tool can help. It creates a circular mask around the eyes, adjusting the image's clarity, exposure, and color temperature.
Additional Tips to Capture the Best Iris Shot
If you follow the steps above correctly, your iris pictures should already look stunning. Yet, we recommend a few more tips to make the shot even more captivating.
Find out our final tips for striking iris photography below!
-
Capture emotions
Ensure your client makes direct eye contact with the camera to create a sense of intimacy and connection. If they struggle to maintain their movement, consider giving the client a prop to focus on. Also, try to capture the shot in a moment of wonder or other genuine emotion to achieve a personality to the photo.
-
Experiment with color and contrast
Although black is the standard background for pictures of eye iris, sticking to the same formula are unnecessary. Based on the eye color of your clients, pick a background tone that compliments the art.
For instance, you can put a fun twist to your iris shot using an orange background for a blue iris. Similarly, don’t waver to play with shadow and light to bring out the details and textures of the iris.
-
Catch the light reflections
As previously mentioned, harsh light can create glare on your images. Hence, we recommend using natural window light or flash with a diffuser. Furthermore, if you notice a small reflection of the light in the pupil, don’t rush to edit it out. It can add a hint of sparkle to the eye, making it look more realistic.
Don’t hesitate to get super close to the eye for dramatic effects when taking pictures of the iris of the eye. It’s also clever to place your light source to the side of the camera instead of its top. In this way, the long lens won’t cast ugly shadows. Alternatively, consider placing it beside the eye if you don’t want light reflecting off the iris.
Lastly, remember to give your clients a few moments to adjust to the light.
Immortalize Your Eyes With Cosmic Eye’s Tailored Iris Photography Services
For hassle-free, unique iris art for you or your loved ones, simply take a few iris photos with your phone or camera and upload them with your order. We’ll handle the editing, printing, and shipping of your one-of-a-kind iris art. Check out our products here: Cosmic Eye Products.